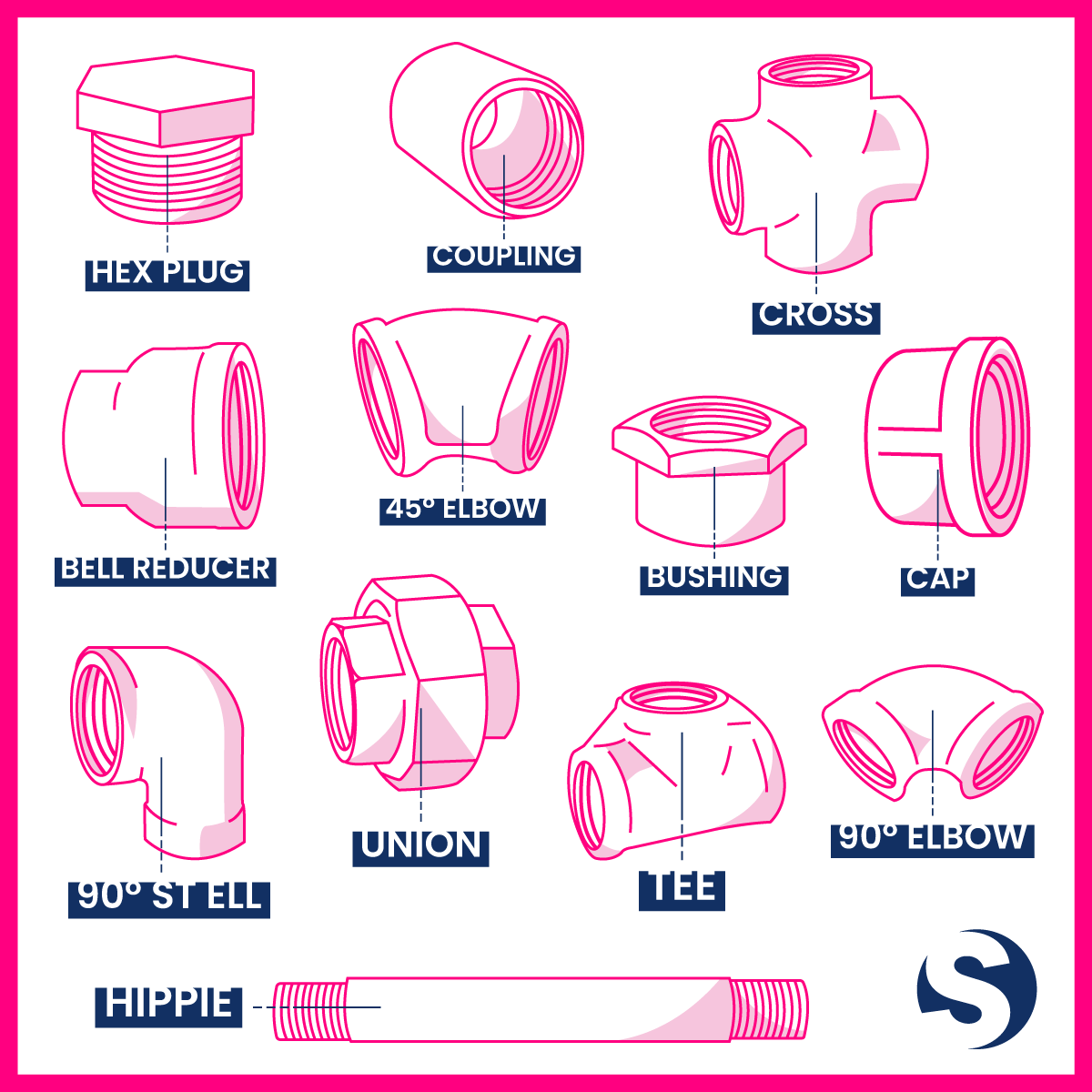
Unless you’re a professional plumber, it’s not easy to make your way through the various plumbing fittings types and make sense of the often-convoluted plumbing terms out there.
Don’t worry – you’re not alone!
At Plumbing Superstore, our customers often ask us:
What are the parts of a pipe fitting called?
To answer this question and help you gain a better understanding of the different types of pipe fittings and plumbing connections, we’ve put together a comprehensive glossary of terms.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
Adaptor: A piping and plumbing fitting used to connect two different types or sizes of pipes or fittings.
B
Ball valve: A type of valve that uses a spherical ball with a hole in it to control the flow of fluid by rotating the ball within a passage.
Barb fitting: A fitting with barbed ends used for connecting hoses or flexible tubing.
Blind flange: A solid flange used to close the end of a pipe or valve.
BSP (British Standard Piping): Globally recognised technical standards for screw threads to enable the secure connection and sealing of pipes and fittings through the mating of male and female threads.
Bulkhead fitting: Used to create a secure connection through a wall or tank.
Bush: A type of fitting with one threaded end and one unthreaded end which is used to connect pipes of different sizes by reducing the size of one end.
Butt weld: A type of weld used to join two pipes or fittings at their ends by melting them together.
C
Cap: Used to close the end of a pipe and provide a seal.
Check valve: A type of valve that allows fluid to flow in only one direction, preventing backflow.
Cleanout: A type of fitting with a removable cap or plug designed to provide access for clearing blockages or cleaning debris from a drainage or sewer pipe.
Compression fitting: Creates a watertight connection by compressing a ring or ferrule onto the pipe.
Corrosion resistance: The ability of a material to withstand chemical reactions that would otherwise cause deterioration.
Coupling: Used to connect two pipes of the same (or similar) size in a straight line.
Cross fitting: A type of plumbing fitting with four openings arranged at right angles to each other which allows for connections in a crosswise configuration.
D
Deflection Temperature (Heat Distortion): A measure used in plumbing systems to determine the temperature at which a plastic material or component begins to deform under a specific load, indicating its ability to withstand elevated temperatures without losing its structural integrity.
Diverter tee: A type of tee with three openings designed to divert the flow of water from one source into two separate directions within a pipe system. Commonly used in shower or bathtub fixtures to control water flow between a showerhead and a bathtub spout.
Dynamic Pressure: The pressure exerted by the moving water within the pipes, resulting from its velocity and kinetic energy. Distinct from static pressure, which is the pressure of water at rest.
E
Elasticity: The ability of the fitting or material to deform under stress and then return to its original shape once the stress is removed, allowing it to accommodate changes in pipe dimensions and absorb mechanical vibrations and shocks.
Elbow: A curved fitting used to change the direction of a pipe, typically at a 90° or 45° angle.
F
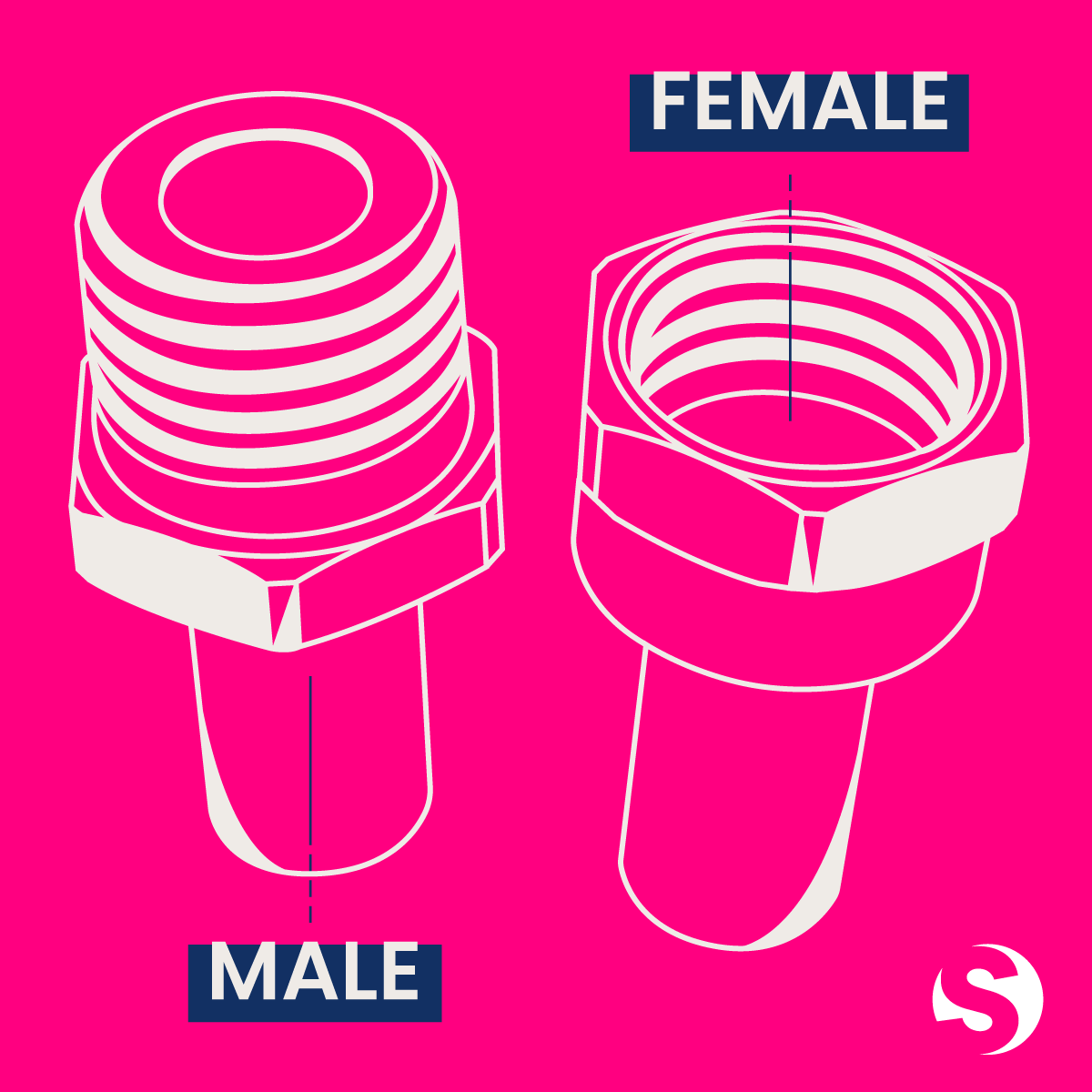
Female thread: The threaded part of a fitting with internal threads designed to receive and be joined with a corresponding male-threaded component.
Fitting: A component or device used in plumbing systems to connect, extend, divert or control the flow of water or other fluids within pipes and tubing, ensuring a secure and watertight connection between various plumbing components.
Flange: A flat, circular fitting with bolt holes used to connect pipes, valves or equipment to form a piping system.
Flange face: The flat surface of a flange where gaskets are placed to create a seal.
Flare fitting: Used to create a leak-free connection between pipes or tubing that carry gases, such as those used in HVAC systems or gas lines, by flaring the end of the pipe and using a flare nut to secure it to another fitting or component.
Flush bush: A type of bush used to create a flush or smooth transition between two pipes or fittings of different sizes. Has one male-threaded end and one smooth, unthreaded end.
G
Gasket: A sealing component placed between flange faces to prevent leaks in a flanged joint.
H
Hose barb: A fitting with a barbed end used to connect hoses to pipes or other equipment.
I
Inner Diameter (ID): The measurement of the distance across the inside of a pipe, tube or conduit which helps determine the flow capacity of the plumbing system.
J
Joint: The point where two or more plumbing components, such as pipes, fittings or fixtures, are connected or joined together to form a continuous and sealed connection within the plumbing system.
K
L
Locking clip: Used to lock together the components of a plumbing fitting or connection, ensuring they remain securely joined and preventing unintended disassembly. Commonly used in push-fit or quick-connect plumbing systems to maintain the integrity of connections without the need for traditional tools or soldering.
M
Male thread: The threaded portion of a pipe, fitting or component that has external threads designed to screw into a corresponding female-threaded opening or fitting, creating a secure and sealed connection when twisted together.
N
Nipple: A short length of pipe or tube with male threads on both ends, used to connect two female-threaded fittings or components, effectively extending or joining sections of a plumbing system.
Nut: A fitting with internal threads used to secure and tighten a threaded connection. Typically pairs with a male-threaded fitting like a bolt to create a secure and leak-free joint by screwing onto the threads and applying pressure to seal the connection.
O
O-ring: A circular, ring-shaped seal typically made from rubber which is used to create a watertight seal between two mating parts within pipe fittings, valves or other plumbing components.
Outer Diameter (OD): The measurement of the distance across the outside of a pipe, tube or conduit. An important parameter to determine the size and compatibility of fittings and connectors.
P
Plug: Used to block or close off the end of a pipe or fitting with a threaded or non-threaded end.
Pressure Rating: The maximum pressure that a fitting or flange can withstand without failing.
Q
Quick connect fitting: Allows for easy and quick connection and disconnection without the need for tools.
R
Reducer: Used to connect two pipes or fittings of different sizes, effectively reducing the diameter or size of the pipe.

S
Sleeve: A cylindrical component, typically made of metal or plastic, used to cover, protect or reinforce a section of a pipe or other plumbing component.
Slip-on flange: A flange with a plain bore that slips over the pipe and is then welded into position.
Socket weld fitting: Used in conjunction with pipes that have socket-weld ends by inserting the pipe into the socket and welding.
Solder: A low-melting-point metal alloy used in plumbing to create a watertight and permanent bond between pipes, fittings and other plumbing components by melting and flowing into the joint to create a sealed connection when it cools and solidifies.
Spigot: A tapered or unthreaded end of a pipe or fitting designed to be inserted into a corresponding socket or hub to create a secure and sealed connection.
Street elbow: A type of elbow with one male-threaded end and one female-threaded end, allowing for a connection between pipes or fittings with different genders or thread types.
Stub end: A short length of pipe with a flared, typically flanged, end which is used to connect pipes with flanged ends, allowing for easy assembly and disassembly of the joint for maintenance or repairs.
Swage nipple: Used to transition from one pipe size to another by concentric or eccentric reduction, typically featuring threaded ends.
T
Tee: A fitting in the shape of the letter T. Has three openings (one inlet and two outlets), allowing for the splitting or combining of the flow of fluid in a plumbing system.
Threaded fitting: Used to easily screw into a pipe, without the need for welding.
Thread sealant: A substance applied to the threads of threaded pipe fittings, valves or pipes to create a tight and leak-free seal when the components are screwed together.
U
Union: A type of pipe fitting consisting of three pieces that can be easily disconnected, allowing for the convenient assembly, disassembly or maintenance of pipes or components in a plumbing system.
V
Valve: A device used to control the flow of fluid within a piping system.
W
Weld neck flange: A type of flange with a long neck that provides reinforcement and is welded to the pipe.
Wye: A Y-shaped fitting with one inlet and two outlets, typically used to divert or combine the flow of fluids in a plumbing system, allowing liquid or gas to flow in two different directions or join two pipes at a 45° angle.
X
Y
Y-Strainer: A type of wye used to remove debris and particles from the flow of fluids in a pipeline.
Z